One comment I often hear from farmers is “I just can’t seem to get an increase in soybean yields as I do for my corn yields.” This is the perfect time of year to reflect on the growing season while analyzing yield results. It’s also the best time to sample for soybean cyst nematodes.
What is SCN?
Soybean cyst nematode is a microscopic ground worm. When analyzing soybean roots, it’s important to correctly identify the difference between nitrogen-fixing nodules and cysts. Nodules for nitrogen production are larger and the size of a pea. Cysts are microscopic and smaller than a grain of sand.
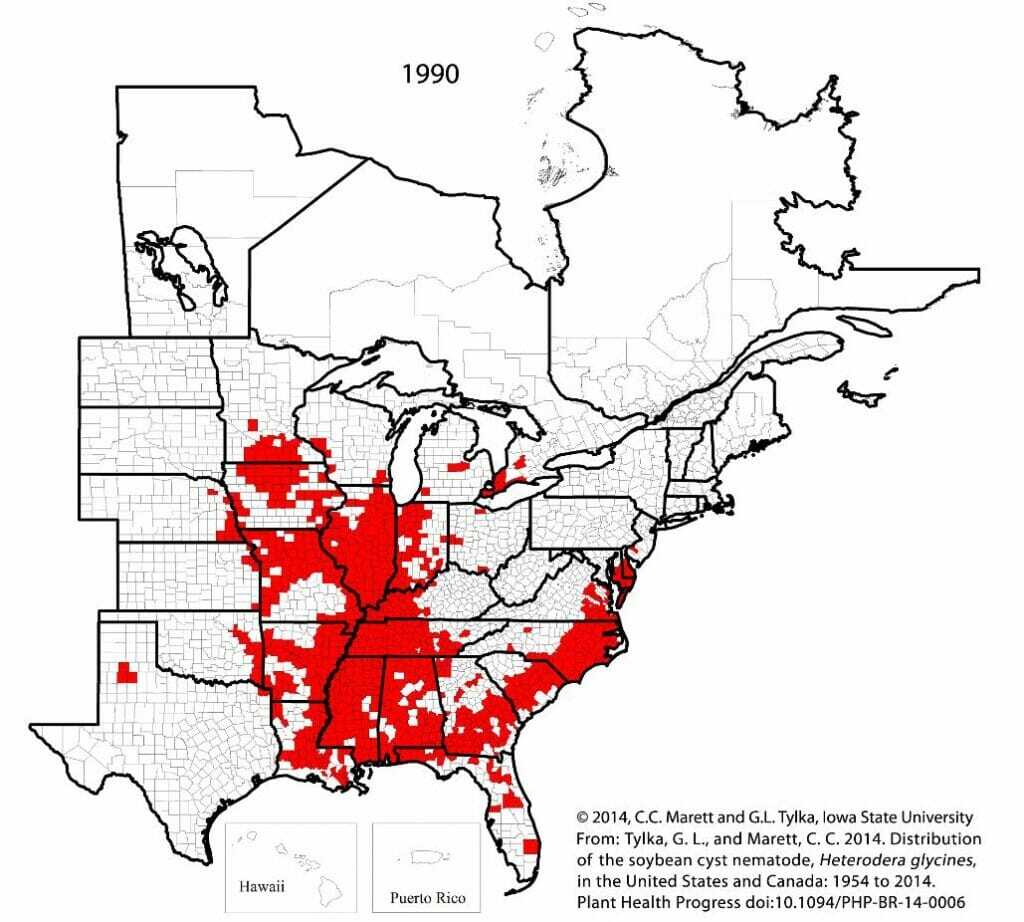
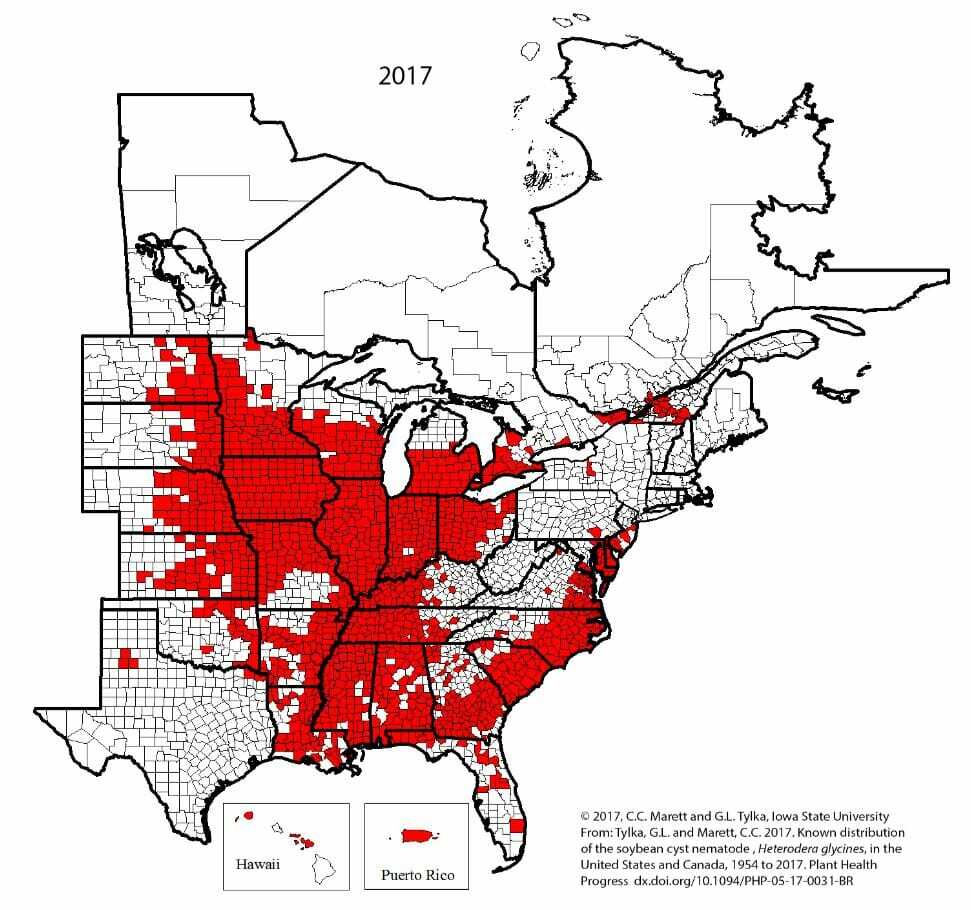
One of the biggest challenges when identifying SCN is that it is not accompanied with many symptoms, but can cause up to a 30% yield loss. Usually SCN shows up in hot spots, where you can see severe stunting, yellowing, shorter crop, lack of canopy or early maturity. These symptoms tend to show up on lighter soil or during tough growing seasons. Wherever soybeans are grown, typically SCN is an issue. Below are two maps to show the growth of SCN over the years.
What is the life cycle of SCN?
Essentially the cyst is the life cycle of a nematode. Juvenile nematodes come in and infect the root. Typically, just the females feed on the root which takes away nutrients from the plants results in a loss of yield. They will then mate and produce eggs. When they produce eggs, they expand in the root, erupt and spread 20 to 500 eggs throughout the soil. The cysts then harden on the root and the process begins again.
In Iowa, we can see that happen for at least three generations per season. Each cyst can have between 20 and 500 eggs inside, creating opportunity for juveniles to come back and begin feeding on the soybean root.
Once the eggs get in the soil, it’s important to understand the number that you have in the soil. Those eggs can stay dormant year-over-year in the soil. Since these eggs are so small, they require very little oxygen to survive.
Management of SCN
The most important management practice of SCN is IPM – Integrated Pest Management. In the Midwest, having a corn and soybean rotation is a great start. Corn is not a host crop whereas soybeans are. I also suggest soil sampling this fall to identify the egg population in your soil. Pull a core from about 8 inches down, right next to the soybean plant right in the root zone.
I also advise to stay away from sampling in the middle of a hot spot for SCN. Often the eggs are concentrated along the edge of the hot spot, so sampling that area will give most accurate results. Population thresholds vary by state. I suggest looking closely to your management practices if results are anywhere from 2,000 – 5,000 eggs per sample. Once you know what is in your field, you can begin to manage it.
Here are three ways to help manage this pest:
- Plant Latham® brand resistant soybeans. Reference product characteristics on our website to identify the disease rating
- Use Latham SoyShield Plus® with Saltro® seed treatment. This will fight SCN and Sudden Death Sydrome.
- TALC USA. Protect corn and soybeans against parasitic nematodes.
Feel free to call into the Latham Seeds office or email me at phill@lathamseeds.com with any questions.